Unlocking Muscle Growth: Training Principles and Physiological Insights
The Science of Muscle Growth
Have you ever wondered what it truly means to grow bigger muscles? Whether for aesthetic appeal or improved strength, muscle growth is a fascinating process deeply rooted in human physiology. This exploration will uncover the biological phenomena behind muscle growth, specifically focusing on hypertrophy—the process where muscle fibers enlarge to increase the overall muscle mass.
What Happens When Muscles Grow?
Muscle hypertrophy is a biological response to certain types of stress, particularly that from resistance training. It involves the enlargement of muscle cells due to an increase in the production of contractile proteins. These proteins are essential for muscle contraction, and their accumulation within the muscle fibers results in an overall increase in muscle size. Understanding this process not only helps in targeting your workouts more effectively but also in appreciating the complex interactions within your body that allow for such transformations.
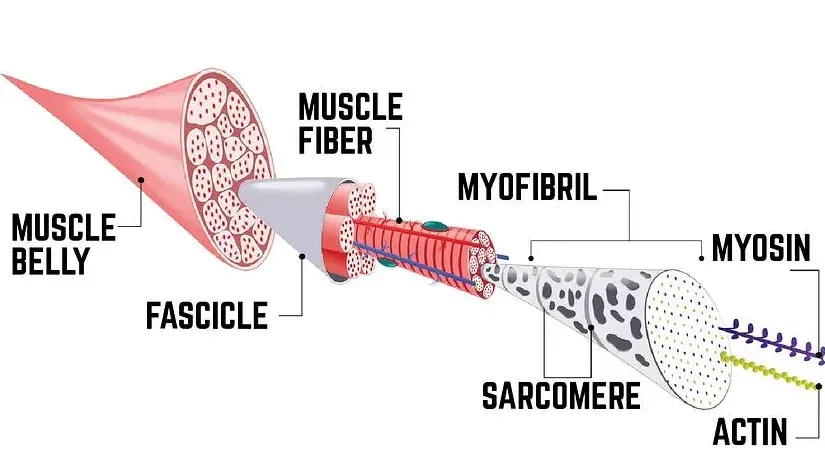
The Types of Muscle Tissue
In discussing muscle growth, it's crucial to recognize the different types of muscle tissue in the body: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal. Each type serves unique functions:
- Smooth Muscle: Found within the walls of organs like the intestines and blood vessels, this muscle type controls the movement of substances through the body, functioning involuntarily.
- Cardiac Muscle: This muscle type is specific to the heart, pumping blood throughout the body autonomously without conscious effort.
- Skeletal Muscle: These are the muscles we commonly train at the gym. They are attached to bones and responsible for voluntary movements and are the primary focus when we talk about muscle growth through exercise.
The Growth Process: Hyperplasia and Hypertrophy
Muscle growth can occur through two different processes:
- Hyperplasia: This process, seen mainly in smooth muscle, involves an increase in the number of muscle cells.
- Hypertrophy: Predominant in skeletal and cardiac muscles, this is the enlargement of existing muscle cells. This understanding is key for anyone looking to increase muscle size through strength training, as it focuses on enhancing the size of these cells rather than increasing their number.
Training Principles for Muscle Growth
Understanding Muscle Fibers
Muscle fibers are essentially the cells that make up our muscles. When we refer to muscle growth in the fitness context, we're specifically talking about the hypertrophy of these fibers. This section will delve into how these fibers adapt to different forms of exercise, fundamentally changing their size and capabilities.
Exercise and Muscle Growth
Resistance training is the cornerstone of inducing muscle hypertrophy. Engaging in specific exercises that challenge your muscles can lead to significant growth over time by consistently stressing the fibers and stimulating biological responses that thicken and strengthen them. Here, we'll break down the essential components of a training regimen designed to maximize muscle growth:
- Strength Training: This method focuses on lifting heavy weights for fewer repetitions. It is designed to increase muscle strength by enlarging the muscle fibers' capacity to exert force.
- Hypertrophy Training: Aimed at increasing muscle mass, this style involves lifting lighter weights for more repetitions. This approach not only enhances the muscle's size but also its endurance.
Practical Insights on Muscle Physiology
Muscle Control and Function
Understanding the control mechanisms of different muscle types adds a layer of depth to our fitness strategies. Smooth muscles operate without our conscious input, managing critical functions in our digestive and circulatory systems. Cardiac muscles, with their intrinsic rhythm, sustain life by pumping blood, and skeletal muscles respond to our commands, allowing movement and strength building through voluntary contractions.
Differences in Growth Potential
The capacity for growth varies significantly across muscle types. Smooth muscle can grow through both hyperplasia and hypertrophy, while cardiac and skeletal muscles primarily enlarge existing cells due to biological constraints that prevent them from multiplying. These distinctions are crucial for tailoring exercise plans that align with physiological possibilities and limitations.
Conclusion: Strengthening Understanding and Physique
Enhancing your knowledge of muscle growth and training principles doesn't just help in achieving aesthetic goals; it also empowers you with the scientific insight to optimize your health and fitness routines. Whether your focus is on strength or size, understanding the underlying mechanisms of muscle function and adaptation can lead to more effective workouts and better overall fitness results.