How the Best Exercise for Improving Blood Pressure Can Transform Your Heart Health
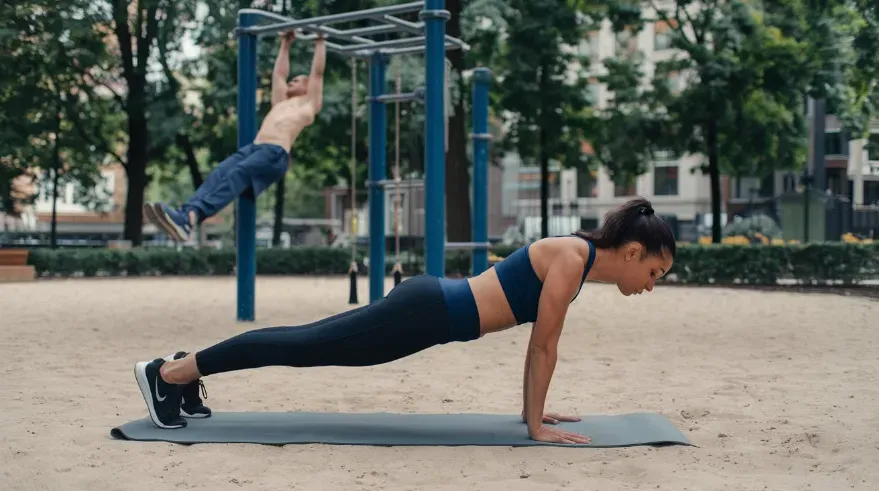
Managing blood pressure effectively can be likened to fine-tuning an orchestra, where each instrument—diet, exercise, and lifestyle—plays a crucial role. The question of which exercise is most beneficial for improving blood pressure has become a focal point for many health enthusiasts. Recently, isometric exercises have come under the spotlight for their potential benefits, rivaling the traditionally favored dynamic exercises. While dynamic exercises promote vascular relaxation and improved circulation, isometric exercises, such as wall sits and planks, offer a fresh perspective on blood pressure management.
To embark on this fitness journey, it’s essential to understand how different exercises impact blood pressure. Dynamic exercises, characterized by continuous movement, enhance cardiovascular efficiency and reduce vascular resistance. Conversely, isometric exercises involve maintaining a static position, which might influence vascular resistance differently. A blend of both exercise types could provide a holistic approach to managing blood pressure, helping you strike a balance between movement and stillness in your fitness routine.
Understanding Blood Pressure and Its Importance
Blood pressure, akin to the rhythm in a musical composition, is crucial in regulating how well your body functions. It measures the force of blood against the walls of arteries, reflecting overall cardiovascular health. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a silent threat, often going unnoticed until serious health issues arise, such as heart disease or stroke.
Managing blood pressure requires a symphony of lifestyle changes and sometimes medication. This orchestrated approach should consider factors like cardiac output and vascular resistance, which are pivotal in maintaining healthy levels. Understanding these elements is key to implementing effective strategies for managing hypertension. Such strategies can include exercise routines tailored to stimulate optimal blood flow and reduce resistance within the vascular system.
Exercise and Blood Pressure Management
Exercise stands as a powerful conductor in the symphony of managing blood pressure, providing benefits that are both immediate and lasting. Dynamic exercises, such as jogging or swimming, facilitate improved heart efficiency and blood vessel relaxation. These activities not only aid in lowering hypertension but also contribute to robust cardiovascular health.
Isometric exercises present a novel method in the quest to control hypertension, yet their efficacy remains a topic of debate. These exercises, characterized by holding static positions, might offer unique benefits to blood pressure regulation that are complementary to dynamic activities. The integration of both exercise styles into a routine can form a comprehensive strategy for achieving optimal blood pressure.
Comparing Dynamic and Isometric Exercises
The comparison between dynamic and isometric exercises centers on how each method influences blood pressure and vascular health. Dynamic exercises promote blood flow through rhythmic movement, supporting vascular relaxation and reducing resistance. Such activities are crucial in maintaining heart health and managing hypertension effectively.
Dynamic Exercises:
- Enhance cardiovascular efficiency.
- Encourage blood vessel relaxation.
- Reduce vascular resistance.
Isometric exercises, on the other hand, involve maintaining muscle tension without movement, presenting a new dimension in blood pressure management. Recent studies suggest they could lower blood pressure, although they challenge the status quo held by dynamic exercises. Including isometric exercises alongside dynamic ones may provide a more rounded approach to fitness.
Isometric Exercises:
- Include static holds like planks.
- Offer potential benefits to blood pressure.
- Should complement dynamic exercises.
Dynamic Exercises and Vascular Relaxation
Dynamic exercises serve as a cornerstone in promoting vascular relaxation, much like a well-conducted symphony allowing each section to shine. As you engage in activities like brisk walking or cycling, your body naturally encourages vasodilation, facilitating blood flow to active muscles. This physiological response aids in reducing vascular resistance, thereby supporting healthy blood pressure levels.
Regular participation in dynamic exercises can help mimic natural bodily functions, improving cardiovascular efficiency and resilience. These exercises not only contribute to lowering hypertension but also enhance overall cardiovascular health, making them indispensable in any blood pressure management regimen.
The Controversy Around Isometric Exercises
Isometric exercises, despite their growing attention, remain a controversial topic in hypertension management. They offer a distinct approach by engaging muscles in static holds, such as in wall sits, which could influence blood pressure differently from dynamic exercises. While these exercises show promise, they often contradict existing research, leading to a need for cautious integration into fitness routines.
Incorporating isometric exercises should be done thoughtfully, acknowledging their potential benefits while not relying solely on them. When combined with dynamic exercises, they can complement a well-rounded fitness strategy aimed at managing hypertension, promoting a balanced approach to cardiovascular health.
Lifestyle Modifications for Hypertension Control
Lifestyle modifications are the foundational notes in the symphony of hypertension management, offering natural ways to control blood pressure before medication is considered. These changes encompass dietary adjustments, like reducing salt and moderating alcohol intake, which significantly impact blood pressure levels. Integrating these interventions can lead to substantial improvements, serving as the bedrock of effective hypertension control.
Adopting regular exercise and ensuring adequate sleep are equally important lifestyle components. Exercise helps regulate vascular resistance, while quality sleep supports the body's restorative processes. Together, these lifestyle modifications form a harmonious approach to achieving and maintaining healthy blood pressure, reducing the risk of serious complications.
Salt and Its Impact on Blood Pressure
Salt intake is a critical factor in hypertension, as excessive sodium consumption can raise blood pressure levels. Your body requires a precise balance of electrolytes for optimal functioning, and too much salt can disrupt this equilibrium. Adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage blood pressure by naturally limiting sodium intake.
For individuals sensitive to salt, even small dietary adjustments can lead to significant blood pressure changes. Reducing sodium should be a primary focus for those striving to maintain or achieve healthy blood pressure levels. This dietary awareness supports cardiovascular health, offering a natural means to regulate blood pressure effectively.
Alcohol Consumption: Moderation is Key
Alcohol consumption is another lifestyle element that can influence blood pressure. While moderate alcohol intake might offer some cardiovascular benefits, excessive consumption is a well-known risk factor for hypertension. This aspect is often overlooked in clinical guidance but remains vital in effective blood pressure management.
Moderate Alcohol Benefits:
- May improve cardiovascular health if consumed responsibly.
- Should be balanced with other health strategies.
Risks of Excessive Alcohol:
- Increases hypertension risk.
- Can interfere with other health management plans.
By adopting a mindful approach to alcohol consumption, individuals can more effectively manage their blood pressure. Limiting intake to recommended levels ensures that alcohol doesn't undermine other lifestyle strategies, enhancing the overall approach to hypertension management.
The Significance of Quality Sleep
Quality sleep is a vital yet often underestimated element in blood pressure management. Poor sleep, especially conditions like sleep apnea, can exacerbate hypertension by disrupting the body's natural processes. Ensuring restful sleep supports cardiovascular health, playing a crucial role in a comprehensive hypertension management strategy.
Sleep disturbances can cause hormonal imbalances, increasing blood pressure and stressing the cardiovascular system. Addressing sleep quality and potential disorders can lead to lower stress levels and improved heart health. This underscores the importance of sleep in managing blood pressure effectively, complementing other lifestyle modifications.
Understanding Sleep Apnea and Its Effects on Blood Pressure
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can significantly affect blood pressure by causing interruptions in breathing during sleep. This can lead to increased cardiovascular strain and heightened blood pressure levels. Addressing sleep apnea with medical intervention can bring substantial improvements in managing hypertension.
For those with hypertension experiencing sleep disturbances, consulting a sleep specialist may provide insights into effective treatment options. By managing sleep apnea, individuals can see remarkable reductions in blood pressure and enhance their overall quality of life. This highlights the crucial connection between sleep and cardiovascular health in hypertension management.
Physiological Insights into Blood Pressure Regulation
Blood pressure regulation involves a complex interplay of physiological processes, primarily governed by cardiac output and vascular resistance. Understanding these mechanisms is essential in developing effective hypertension management strategies. Exercise, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions all interact to influence these factors, contributing to improved blood pressure control.
The interaction between cardiac output and vascular resistance highlights the necessity of a comprehensive approach to managing hypertension. Addressing these physiological elements through targeted strategies empowers individuals to achieve more sustainable blood pressure levels. This foundational understanding informs decisions about exercise regimens and lifestyle modifications, offering a pathway to enhanced heart health.
The Science Behind Vascular Resistance and Cardiac Output
Cardiac output and vascular resistance are the cornerstones of blood pressure regulation, serving as primary determinants. Cardiac output, the volume of blood the heart pumps per minute, and vascular resistance, the resistance encountered by blood flow, together influence blood pressure levels. Targeting these elements is vital in any effective hypertension management plan.
Regular physical activity and a heart-healthy lifestyle positively impact both cardiac output and vascular resistance. Exercise strengthens the heart, improving circulation and reducing resistance, while diet supports vascular health. Understanding these mechanisms empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, enhancing the effectiveness of hypertension management strategies.
The Phenomenon of Functional Sympatholysis
Functional sympatholysis is the body's natural process by which exercising muscles release metabolites to counteract sympathetic nerve-induced constriction. This process facilitates vasodilation in active muscles, promoting blood flow and reducing vascular resistance. It is a critical component in how exercise positively influences blood pressure regulation.
Understanding functional sympatholysis offers valuable insights into why dynamic exercises are particularly effective for hypertension management. The body's ability to balance constriction and dilation underscores the importance of regular exercise in maintaining healthy blood pressure. This knowledge reinforces the necessity of integrating exercise into comprehensive hypertension management strategies.
Beyond Exercise: Comprehensive Strategies for Hypertension
Exercise is an essential piece in the puzzle of managing hypertension, but it must be complemented by broader strategies that include dietary changes and regular health screenings. Addressing all aspects of lifestyle offers a holistic approach, providing the best chance for reducing blood pressure and associated health risks.
A comprehensive strategy involves understanding individual risk factors and tailoring interventions accordingly. This could involve monitoring hormone levels or making specific dietary changes, such as increasing potassium intake. By considering the full spectrum of lifestyle and health factors, individuals can effectively manage hypertension and support their overall well-being.
Dietary Changes and Nutrient Intake
Dietary modifications are a critical part of a comprehensive strategy for managing hypertension. Beyond reducing salt and alcohol, increasing the intake of potassium-rich foods helps balance electrolytes and supports healthy blood pressure levels. Foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens are excellent choices for maintaining cardiovascular health.
Dietary Focus:
- Increase fruits and vegetables.
- Choose whole grains and lean proteins.
- Limit processed foods and sugars.
Incorporating diverse nutrients into one's diet supports cardiovascular health and enhances the body's ability to regulate blood pressure. By emphasizing whole, minimally processed foods and maintaining a balanced diet, individuals can support their overall health and manage hypertension effectively.
The Importance of Monitoring Hormonal Levels
Hormonal imbalances can significantly influence hypertension, particularly conditions like hyperaldosteronism, which involves excess production of aldosterone. This hormone raises blood pressure by retaining sodium and water, making monitoring these levels crucial for targeted treatments and improving hypertension management.
Regular health screenings and blood tests can reveal hormonal abnormalities, guiding appropriate interventions. Addressing these underlying causes can lead to more effective hypertension management and potentially reduce the need for medication. Understanding hormones' role in blood pressure regulation is a crucial aspect of managing this common health condition.
Can Lifestyle Interventions Reverse Hypertension?
Reversing hypertension through lifestyle interventions depends on several factors, including the severity and stage of the condition. In cases of mild hypertension, especially among younger individuals, targeted lifestyle changes can lead to significant improvements. By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes exercise, dietary changes, and quality sleep, individuals can work towards better blood pressure control.
It's important to recognize that lifestyle interventions might not suffice for everyone. Those with advanced or long-standing hypertension may still require medication alongside lifestyle changes. The key lies in tailoring interventions to individual needs, balancing lifestyle modifications with medical guidance for optimal results.
Potential in Mild and Early-Stage Hypertension
For those with mild or early-stage hypertension, lifestyle interventions can be particularly effective. By embracing healthy habits such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, individuals often reduce their blood pressure to normal levels without medication. These foundational changes promote long-term cardiovascular health.
Early Intervention Benefits:
- Prevents disease progression.
- Reduces medication dependency.
- Encourages sustainable health improvements.
Early intervention is crucial in preventing the progression of hypertension. By addressing risk factors and implementing positive lifestyle changes sooner rather than later, individuals can often stave off the need for medication and its associated side effects, leading to sustained improvements in blood pressure management and overall well-being.
Special Considerations for Different Age Groups
Different age groups experience varying benefits from lifestyle interventions in managing hypertension. Younger individuals may find it easier to reverse hypertension through lifestyle changes alone, whereas older adults might need a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Age-specific factors, such as hormonal changes and metabolic rate, influence how effectively lifestyle interventions work.
Older adults, in particular, should focus on maintaining cardiovascular fitness through age-appropriate exercises and monitoring their diet closely. Additionally, addressing any age-related health issues, such as sleep apnea or metabolic disorders, can enhance hypertension management strategies' effectiveness. Tailoring interventions to specific age-related needs ensures a more personalized and successful approach to managing blood pressure.
Conclusion: Crafting a Balanced Approach to Blood Pressure Management
Managing blood pressure effectively requires a balanced approach that combines exercise, lifestyle modifications, and, when necessary, medical interventions. Understanding the physiological underpinnings of blood pressure regulation and tailoring interventions to individual needs empowers individuals to achieve better health outcomes. By integrating regular exercise, dietary changes, and mindful lifestyle choices, you can create a comprehensive strategy to support cardiovascular health and manage hypertension.
The journey toward better blood pressure control is personal, requiring dedication and consistency. By incorporating evidence-based strategies and remaining informed about the latest research, individuals can make empowered decisions about their health. A balanced approach not only effectively manages hypertension but also enhances overall quality of life, paving the way for a healthier future.
