The Surprising Health Benefits of Ancient Grains vs. Modern Wheat
Introduction to the Impact of Diet on Health
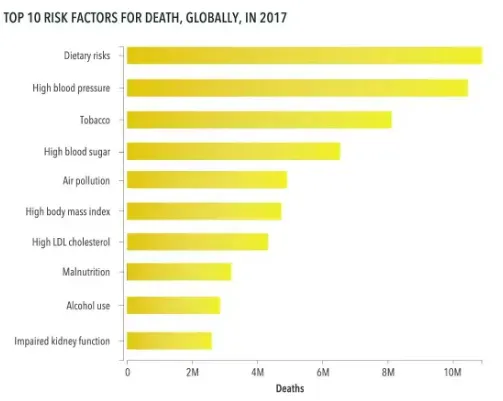
Understanding the Global Dietary Crisis
Dietary habits play a significant role in global health, with poor choices linked to millions of premature deaths each year. Research indicates that diets high in processed foods and low in whole foods contribute heavily to the prevalence of diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and strokes. These issues underscore the global need for significant dietary changes, focusing on both increased awareness and better accessibility to healthier food options.
Key Dietary Changes for Optimal Health
Adjusting our diets based on recent scientific findings is one of the most effective health strategies. Recommended dietary changes for optimal health include:
- Reducing sodium intake to mitigate blood pressure and heart disease risks.
- Increasing intake of nuts which are rich in essential fats and proteins.
- Incorporating more non-starchy vegetables which provide essential vitamins and minerals with lower calorie counts.
- Adding more fruits to the diet, which offer vitamins and antioxidants.
- Consuming more whole grains which are beneficial for digestive health and maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
These dietary adjustments not only aim to minimize the risk of chronic diseases but also enhance overall well-being, supporting both physical and mental health.
Exploring Ancient Grains
What are Ancient Grains?
Ancient grains are defined as grains that have been little changed by selective breeding over the millennia. Kamut (Khorasan wheat) and Einkorn are prime examples. These grains are highly valued for their minimal processing and high nutrient content, as opposed to modern wheat varieties which have undergone extensive breeding to enhance certain traits like yield and size.
Historical Context and Modern Reintroduction
Historically, ancient grains were staples in ancient civilizations' diets but gradually fell out of favor due to the rise of more commercially profitable modern grains. In recent years, there has been a significant resurgence in the popularity of these grains as more consumers seek out food options that are not only healthier but also sustainable. This revival is part of a larger movement towards traditional dietary practices, believed to be more in alignment with human health needs.
Examples of Ancient Grains: Kamut and Einkorn
- Kamut: Known for its rich, nutty flavor; often used in bread, pasta, and cereal.
- Einkorn: Recognized as the oldest form of wheat available, with a dense nutrient profile and deep, complex flavor.
These grains are favored not just for their distinctive taste but also for their superior nutritional value.
Nutritional Profile of Ancient Grains
Ancient grains generally boast a higher concentration of nutrients compared to modern wheat varieties. They offer:
- Increased antioxidants
- Higher levels of vitamins and minerals
- Enhanced fiber content
All of which contribute to broader health benefits ranging from improved digestive health to reduced chronic disease risk.
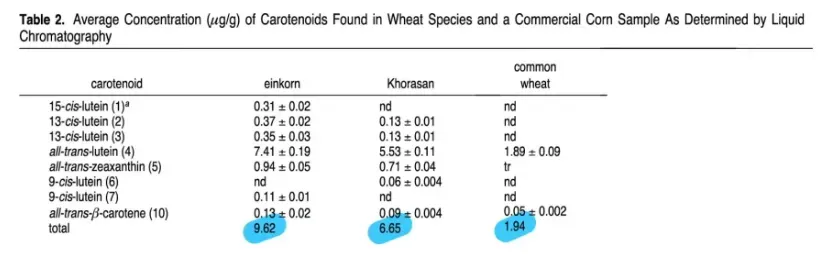
Carotenoids in Ancient Grains
Ancient grains, such as Kamut and Einkorn, are especially rich in carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin—compounds renowned for their benefits to eye health. The prominence of these pigments in ancient grains is due to lesser breeding focus on aesthetic traits like flour color, which is a common practice for modern wheat varieties.
Antioxidant Content and Its Implications
The higher antioxidant content in ancient grains can be attributed to the minimal processing they undergo. These antioxidants, including various polyphenols, are crucial for:
- Reducing oxidative stress
- Combatting inflammation
- Supporting overall cellular health
This enhanced antioxidant capacity suggests that ancient grains could offer more significant health benefits than modern wheat varieties, particularly in terms of reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Comparative Analysis of Ancient vs. Modern Wheat
Nutritional Differences: Vitamins and Minerals
Both ancient and modern wheats offer beneficial nutrients; however, ancient grains often provide a broader spectrum of vitamins and minerals. This includes higher levels of:
- Magnesium: Essential for over 300 biochemical reactions in the body.
- Potassium: Vital for heart function and normal cellular function.
- Antioxidants: Important for preventing damage from free radicals.
Impact on Inflammation and Human Health
Studies have indicated that ancient grains can potentially reduce inflammation more effectively than modern wheat. This is likely due to their higher polyphenol content, which plays a pivotal role in modulating the body's inflammatory pathways. Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for many serious health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer, making the anti-inflammatory properties of ancient grains especially beneficial.
Ancient Grains and Chronic Health Conditions
Effects of Ancient Grains on Inflammatory Diseases
Clinical trials have provided evidence that diets rich in ancient grains like Kamut may help reduce symptoms associated with inflammatory health conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Participants have reported:
- Reduced abdominal pain
- Decreased bloating
- Enhanced overall digestive comfort
These improvements highlight the potential of ancient grains to not only manage but possibly improve symptoms associated with inflammatory diseases.
Benefits for Metabolic Health
Including ancient grains in the diet has also been linked with improved metabolic health markers. Studies have shown that these grains can help:
- Improve cholesterol levels
- Enhance blood sugar control
- Reduce markers of inflammation
These benefits make ancient grains a strong dietary option for those managing or at risk for metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Practical Advice for Incorporating Ancient Grains
How to Integrate Ancient Grains into Your Diet
To start incorporating ancient grains into your diet, try substituting a portion of your daily grain intake with ancient varieties. For example, replace modern wheat bread with bread made from spelt or Kamut. Additionally, exploring different ancient grains can add variety to your meals and boost your nutrient intake.
Identifying Authentic Ancient Grain Products
When shopping for ancient grains, look for products labeled as "whole grain" to ensure you're receiving the full nutritional benefits. It's also beneficial to purchase from sources that adhere to sustainable and organic farming practices, maximizing the health benefits and supporting environmentally friendly agriculture.
Simple Recipes and Meal Ideas
Here are a few ways you can incorporate ancient grains into your meals:
- Breakfast: Try ancient grain porridges or pancakes.
- Lunch: Use ancient grains in salads or soups for a nutritious boost.
- Dinner: Replace traditional rice or pasta with ancient grains like quinoa or farro.
Precautions and Considerations
While ancient grains are generally beneficial, it's important to introduce them into your diet gradually, especially if you have existing health issues or food sensitivities. Consulting with a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes is advisable to ensure that ancient grains are a suitable addition to your diet.
Conclusion
Summarizing the Benefits of Ancient Grains
Ancient grains offer a wealth of health benefits due to their superior nutritional content and minimal processing. Their resurgence in the modern diet is a testament to their enduring value and potential to improve health outcomes.
Future Outlook and Research Needs
The growing popularity of ancient grains highlights the need for more comprehensive research to fully understand their health benefits and potential applications. As more data becomes available, ancient grains could play an increasingly significant role in global dietary recommendations, potentially helping to address some of the pressing health issues related to modern dietary practices.
References:
- Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;393(10184):1958-1972.
- Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017 Infographic
- Shewry PR. Do ancient types of wheat have health benefits compared with modern bread wheat?. J Cereal Sci. 2018;79:469–476.
- Bordoni A, Danesi F, Di nunzio M, Taccari A, Valli V. Ancient wheat and health: a legend or the reality? A review on KAMUT khorasan wheat. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2017;68(3):278-286.
- Dinu M, Whittaker A, Pagliai G, Benedettelli S, Sofi F. Ancient wheat species and human health: Biochemical and clinical implications. J Nutr Biochem. 2018;52:1-9.
- Abdel-Aal el-SM, Young JC, Rabalski I, Hucl P, Fregeau-reid J. Identification and quantification of seed carotenoids in selected wheat species. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55(3):787-94.
- El-Sayed M. Abdel-Aal, Iwona Rabalski. Bioactive Compounds and their Antioxidant Capacity in Selected Primitive and Modern Wheat Species. The Open Agriculture Journal. 2008;2:7-14.





